Understanding Inositol: From Cell Health to Hormone Support
Quick Facts for Busy Readers
| Topic | Key Points |
| What it is | A sugar-like compound vital for cell growth and insulin signaling |
| Benefits | Supports mood, blood sugar balance, fertility, and metabolic health |
| Dosage | Varies by condition: 1–18g daily |
| Common Forms | Capsules, tablets, gummies |
| When to Take | After meals—morning and evening |
| Side Effects | Rare: nausea, fatigue, diarrhea |
| Drug Interactions | May increase risk of hypoglycemia with diabetes medications |
| Important Note | Always consult your healthcare provider before starting inositol supplements |
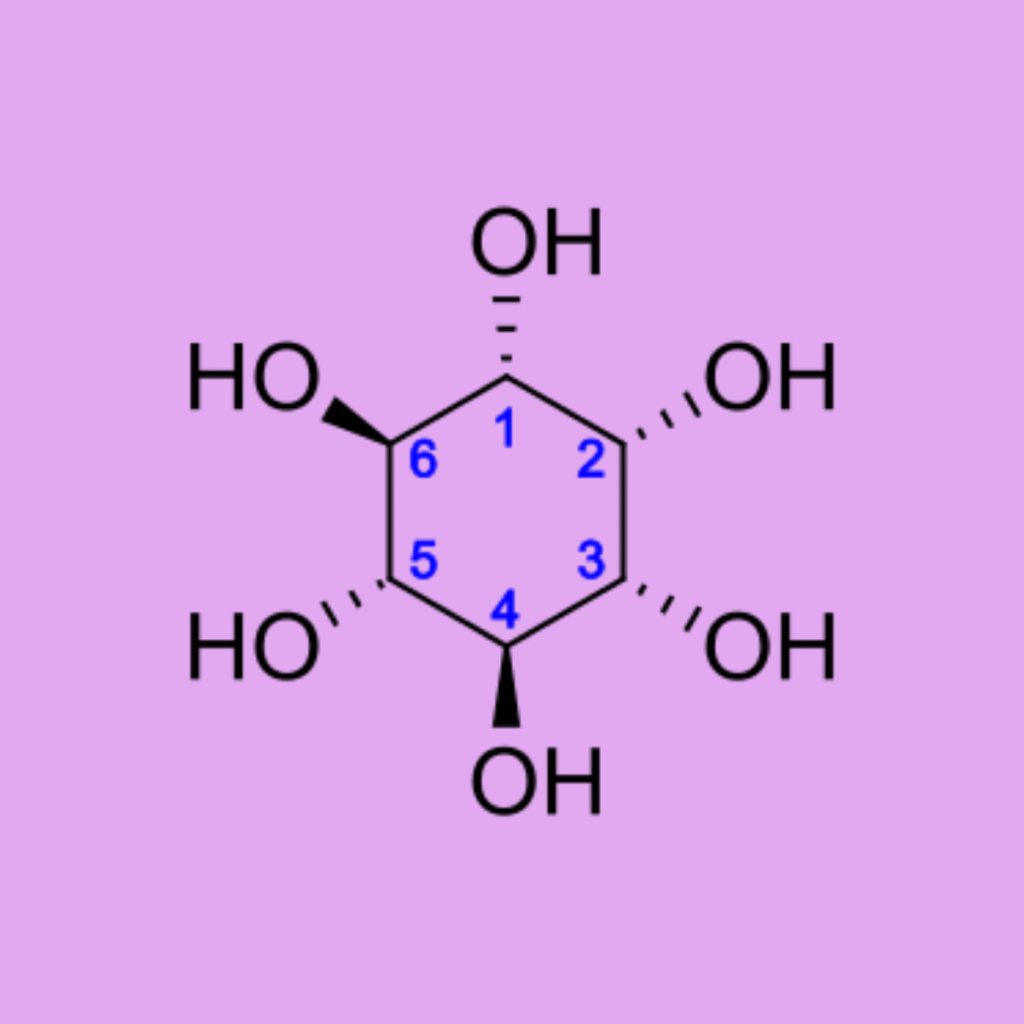
What Is Inositol?
Also known as:
Vitamin B8, Myo-inositol, D-chiro-inositol, Inositol hexaphosphate
Inositol is a carbocyclic sugar naturally found in your body and in certain foods. It plays a key role in cell membrane formation and signaling, insulin regulation, and neurotransmitter balance.
What Is Inositol Good For?
Inositol may help with:
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
- Gestational Diabetes & Type 2 Diabetes
- Metabolic Syndrome
- High Cholesterol
- Mood Disorders such as anxiety and depression
- Improved insulin sensitivity
- Hormonal balance and ovulation support
Where does Inositol Comes From
Inositol is naturally found in:
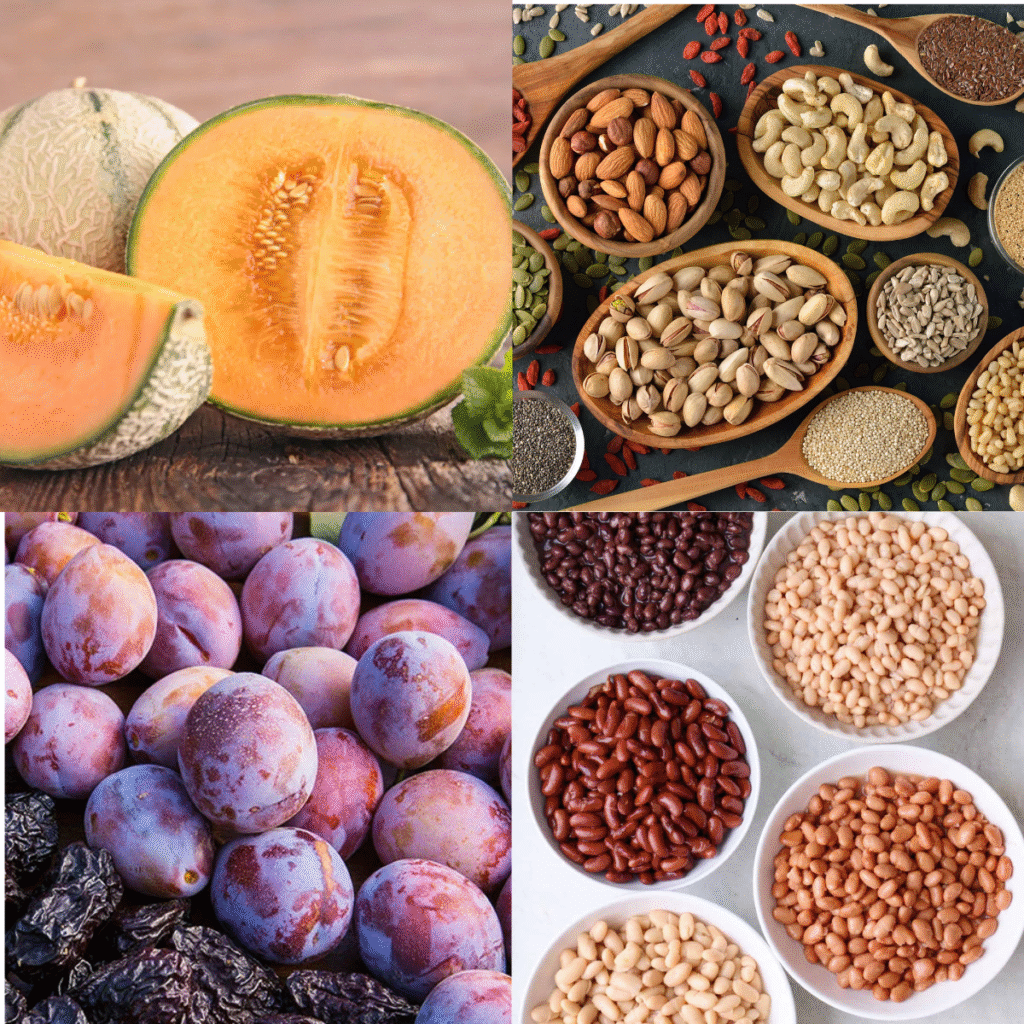

- Citrus fruits (especially cantaloupe)
- Prunes, beans, peas
- Whole grains like brown rice and wheat bran
- Nuts and seeds
How does Inositol Works (Mechanism of Action)
Inositol improves insulin signaling by acting as a second messenger, helping regulate glucose uptake and hormonal balance. It also affects neurotransmitter function, which may support mental health.
Signs You Might Need Inositol
Possible symptoms of inositol deficiency:
- Mood instability, anxiety, or sleep issues
- Constipation
- Muscle weakness
- High cholesterol or blood lipid levels
Best Forms & Absorption (Bioavailability)
- Myo-inositol: most bioavailable and commonly used form
- D-chiro-inositol: often combined with myo-inositol in PCOS treatment
- Best absorption: when taken after meals, ideally morning and night
How Much Inositol to Take (Dosage)
| Use Case | Dosage |
| PCOS | 2g myo-inositol + 200 mcg folic acid, twice daily (6 months) |
| Mental Health | 12–18g daily for 4–6 weeks |
| Metabolic Syndrome | 2g myo-inositol, twice daily for 12 months |
| Gestational Diabetes | 2g inositol + 400 mcg folic acid, twice daily during pregnancy |
| Type 2 Diabetes | 1g D-chiro-inositol + 400 mcg folic acid once daily (6 months) |
When to Take Inositol
- Take after meals, preferably with breakfast and dinner, for optimal insulin and hormone support.
Side Effects
Inositol is generally well tolerated.
Possible side effects (rare):
- Abdominal discomfort
- Nausea
- Diarrhea
- Fatigue
Can Inositol Interact With Medications?
Yes — inositol may enhance insulin sensitivity, increasing the risk of hypoglycemia if you’re on diabetes medication.
Important: Always consult your doctor or pharmacist before combining inositol with prescription medications.
Extra Tips
- Consistency is key—take your dose daily, ideally after meals
- Combine with folic acid for added benefits, especially in PCOS and pregnancy support
- Pairing with a balanced diet and healthy lifestyle enhances results
Inositol offers powerful support for blood sugar, fertility, and mental health—but only if you use it right. Start with the recommended dose, stay consistent, and check in with your doctor to unlock its full benefits.
Don’t wait to take control of your health! Whether it’s managing PCOS, balancing blood sugar, or boosting mood, Inositol can help.