The Ultimate Guide To Vitamin C :All You Need To Know

Quick Facts for Busy Readers
| Topic | Key Points |
|---|---|
| What it is | Water-soluble vitamin needed daily for immune function, antioxidant protection |
| Also Known As | L-ascorbic acid |
| Benefits | Boosts immunity, improves skin, supports heart and eye health, helps absorb iron |
| Sources | Citrus fruits, berries, kiwi, guava, rose hips, acerola cherries |
| Dosage | 75–90 mg/day for adults; up to 2,000 mg short-term |
| Best Forms | Liposomal Vitamin C (most bioavailable) |
| When to Take | On an empty stomach, preferably in the morning |
| Side Effects | GI upset at high doses |
| Drug Interactions | May interfere with warfarin, estrogens, levothyroxine, niacin |
| Important Note | Always consult your healthcare provider if taking medication |
When people think of Vitamin C, they often think of orange juice and immunity, but this powerhouse nutrient does far more than just help you recover from a cold. Also known as L-ascorbic acid, Vitamin C is a water-soluble vitamin essential for tissue repair, collagen synthesis, immune defense, and antioxidant protection.
Vitamin C is critical—especially for children, athletes, older adults, and anyone under stress. Let’s explore everything you need to know to get the most out of this vital nutrient.
What Is Vitamin C?
- Name: Vitamin C
- Also Known As: L-ascorbic acid
- What It Is: A water-soluble vitamin crucial for tissue growth and repair, antioxidant protection, and immune support. Since humans can’t produce it, daily intake from food or supplements is essential.
Your body can’t make or store Vitamin C, so you need a daily supply from your diet or supplements.
What Is Vitamin C Good For
Vitamin C supports the body in many ways:
- Immune defense: Stimulates white blood cell activity
- Wound healing: Supports collagen production
- Heart health: May reduce blood pressure and heart disease risk
- Eye health: Supports retinal health and prevents oxidative damage
- Iron absorption: Enhances non-heme iron absorption
- Skin health: Brightens and protects against environmental damage
- Joint support: May reduce inflammation in joints
Where Vitamin C Comes From
Top Vitamin C-rich foods include:
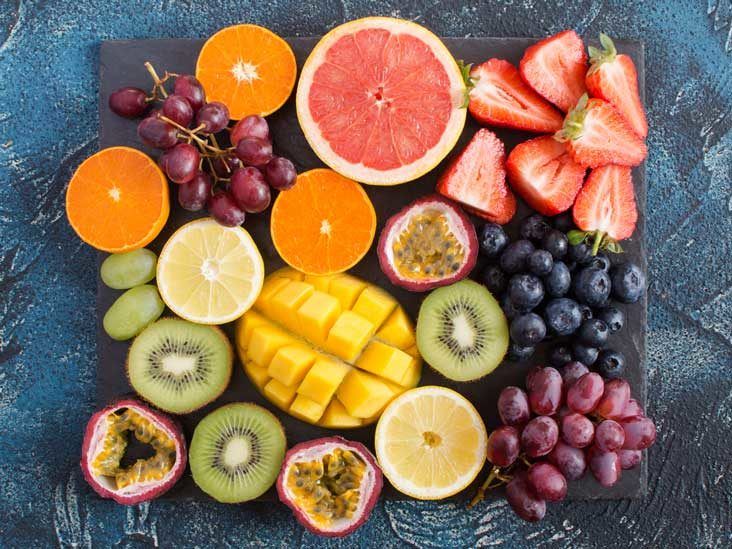

- Citrus fruits (oranges, lemons, grapefruits, limes)
- Strawberries
- Kiwi
- Cantaloupe
- Guava
- Kakadu plums (extremely rich source)
- Acerola cherries
- Rose hips
How Vitamin C Works (Mechanism of Action)
Vitamin C helps your body by:
- Neutralizing free radicals as an antioxidant
- Supporting collagen synthesis (important for skin, joints, and blood vessels)
- Aiding neurotransmitter production like dopamine and serotonin
- Boosting immune response by protecting white blood cells

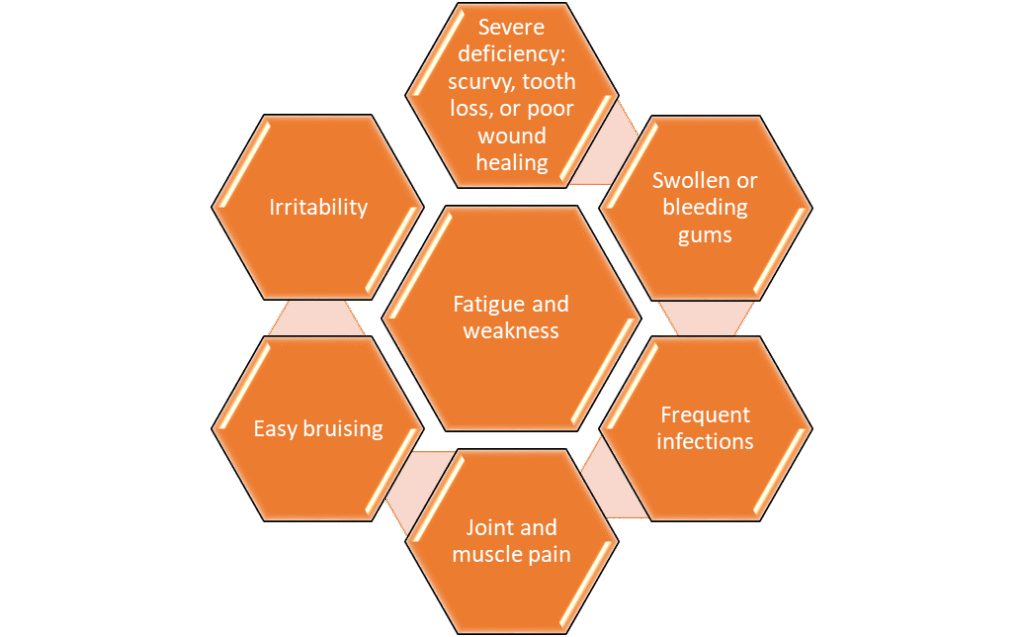
Signs You Might Need Vitamin C
Symptoms of deficiency may include:
Best Forms & Absorption (Bioavailability)
| Form | Notes |
|---|---|
| Liposomal Vitamin C | Highly bioavailable and easy on the stomach |
| Buffered Vitamin C | Great for sensitive stomachs (combined with minerals) |
| Ascorbic acid | Affordable and commonly used |
| Effervescent tablets | Fast absorption, easy to digest |
| Gummies | Kid-friendly and chewable |
Absorption Tips:
- Take on an empty stomach (morning or 2 hours after eating)
- Split large doses throughout the day for better uptake
How Much Vitamin C To Take (Dosage)
Recommended Daily Intake:
| Life Stage | Dose |
|---|---|
| Birth–6 months | 40 mg |
| 7–12 months | 50 mg |
| Children 1–3 yrs | 15 mg |
| Children 4–8 yrs | 25 mg |
| Children 9–13 yrs | 45 mg |
| Teens (boys) | 75 mg |
| Teens (girls) | 65 mg |
| Adults (men) | 90 mg |
| Adults (women) | 75 mg |
| Pregnant teens | 80 mg |
| Pregnant women | 85 mg |
| Breastfeeding teens | 115 mg |
| Breastfeeding women | 120 mg |
Short-Term Immune Support:
| Group | Daily Upper Limit |
|---|---|
| Kids 1–3 yrs | 400 mg/day |
| Kids 4–8 yrs | 650 mg/day |
| Teens 9–13 yrs | 1,200 mg/day |
| Teens 14–18 yrs | 1,800 mg/day |
| Adults | Up to 2,000 mg/day |
Available Form:

- Capsules
- Gummies
- Powders
- Liposomal liquids
- Effervescent tablets
When to Take Vitamin C
- Best time: Morning on an empty stomach
- Take 2 hours after eating if not in the morning
- Avoid taking large doses at night—it may disrupt sleep
Side Effects (If Any)
| High dose may cause: | |
|---|---|
| Nausea | Vomiting |
| Stomach cramps | Heartburn |
| Diarrhea | Bloating |
Most side effects occur with intakes above 2,000 mg/day
Who Should Be Careful
Caution is advised for:
- Those with kidney stones or high oxalate levels
- People on specific medications (see interactions below)
Can Vitamin C Interact With Medications?
| Medication | Effect |
|---|---|
| Estrogens | May slow breakdown, increasing hormone levels |
| Niacin | May blunt effects on HDL cholesterol |
| Warfarin | May reduce blood-thinning effect — monitor INR |
| Levothyroxine | May increase hormone levels — monitor carefully |
Always consult your doctor or pharmacist before supplementing.
Bonus Tips
- Pair with iron-rich meals to improve iron absorption
- Combine with Vitamin E and zinc for full-spectrum immune support


Tips To Optimize Your Vitamin C:
- Choose liposomal or buffered forms for best absorption
- Take on an empty stomach for maximum effect
- Use higher doses short-term when needed (up to 2,000 mg)
- Be aware of drug interactions and kidney health risks
Should You Take Vitamin C?
Vitamin C is essential for immunity, glowing skin, heart health, and tissue repair. While most people get some from their diet, supplements can offer an extra boost during illness, stress, or nutrient gaps.

