The Ultimate Guide To Omega 3 :All You Need To Know

Omega 3 supplements have gained significant attention for their wide range of health benefits, from supporting brain function to reducing inflammation.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through what omega fatty acids are, what they’re good for, how they work, how much to take, and more.
| Topic | Omega-3 Fatty Acids |
|---|---|
| Key Points | Essential polyunsaturated fats that support brain, heart, eye, and joint health while reducing inflammation. |
| What it is | Healthy fats (EPA, DHA, ALA) vital for brain function, cell structure, and anti-inflammatory balance. |
| Also Known As | Fish Oil, Omega-3, n-3 Fatty Acids |
| Benefits | Supports brain and heart health, reduces inflammation, promotes healthy skin and eyes, improves mood, and aids joint flexibility. |
| Sources | Salmon, tuna, mackerel, sardines, chia seeds, flaxseeds, walnuts, avocados. |
| Dosage | General: 250–500 mg combined EPA + DHA daily; for high triglycerides: 2–4 g daily (under medical supervision). |
| Best Forms | Re-esterified triglyceride (rTG) form — highest bioavailability; also available as ethyl ester (EE) and phospholipid (krill oil). |
| When to Take | With a meal containing healthy fats to enhance absorption. |
| Side Effects | Mild GI discomfort (belching, indigestion, fishy aftertaste); possible bleeding risk at very high doses. |
| Drug Interactions | May increase effects of anticoagulants (warfarin) and antiplatelet drugs (aspirin, ibrutinib). |
| Important Note | Consult your healthcare provider before use if on blood thinners or preparing for surgery. |
What Is Omega 3?
- Name: Omega
- Also known as: Omega 3
- What it is: Omega-3 fatty acids are a type of polyunsaturated fat, essential for various bodily functions and overall health.
What Is Omega 3 Good For

| Benefit Area | Key Points |
|---|---|
| Brain Function | Omega-3s are crucial for brain development and function. They may enhance learning, memory, and cognitive well-being. |
| Inflammation | Omega-3s possess anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce inflammation throughout the body. This can be beneficial for conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, and other inflammatory conditions. |
| Mental Health | Some studies suggest that omega-3s may help improve mood and reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety. |
| Eye Health | Omega-3s may help protect against age-related macular degeneration and dry eye syndrome. |
| Other Benefits | Omega-3s may also help promote healthy skin, improve sleep quality, and support overall well-being. |
Where Omega 3 Comes From

- Salmon
- Tuna
- Mackerel
- Sardines.
- Avocado
How Omega 3 Works (MOA)
Particularly eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), exert their effects through various mechanisms, including influencing gene expression, modulating inflammatory responses, and altering cell membrane composition.
Signs You Might Need Omega 3
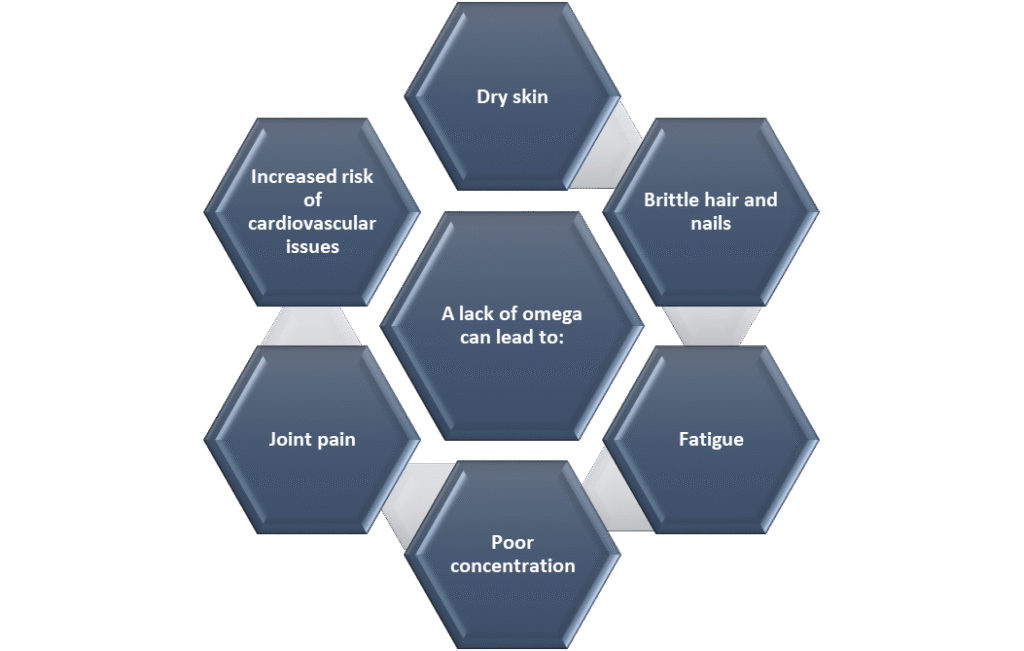
Other potential signs include mood swings, anxiety, and depression. Some individuals may also experience excessive earwax buildup, dry eyes, and difficulty with wound healing.
Best Forms & Absorption (Bioavailability)
- Easier to absorb forms: The re-esterified triglyceride (rTG) is the most bioavailable form of omega-3.
- Tips to boost absorption: Best taken with a meal, especially one containing healthy fat.
How Much Omega 3 to Take (Dosage)
General Recommendation
| Age | Male | Female | Pregnancy | Lactation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Birth to 6 months* | 0.5 g | 0.5 g | ||
| 7–12 months* | 0.5 g | 0.5 g | ||
| 1–3 years** | 0.7 g | 0.7 g | ||
| 4–8 years** | 0.9 g | 0.9 g | ||
| 9–13 years** | 1.2 g | 1.0 g | ||
| 14–18 years** | 1.6 g | 1.1 g | 1.4 g | 1.3 g |
| 19–50 years** | 1.6 g | 1.1 g | 1.4 g | 1.3 g |
| 51+ years** | 1.6 g | 1.1 g |
Tips : Take with a fatty meal 1–3 times per day.
Hypertriglyceridemia (adjunctive agent):
Oral: 4 g once daily or 2 g twice daily
Side Effects
Mainly Gastrointestinal:
- Dysgeusia (taste disorder)
- Dyspepsia
- Eructation (belching or burping)
Can Omega 3 Interact With Medications?
- Anticoagulants: Omega-3 Fatty Acids may increase anticoagulant effects of anticoagulants.
- Ibrutinib: Omega-3 Fatty Acids may increase antiplatelet effects of Ibrutinib.
- Therapeutic Antiplatelets: Omega-3 Fatty Acids may increase antiplatelet effects of therapeutic antiplatelets.
Important: Always check with your healthcare provider.
Conclusion
Omega-3s are essential for overall health, offering a range of benefits from brain support to inflammation reduction. Whether you’re considering supplementation for a specific health condition or as a general wellness practice, understanding the correct dosage and form can make a big difference.
If you found this guide helpful, be sure to bookmark it or share it with someone who might benefit.
Start your Jouney today with Omega 3 and unlock It’s many health benefits to enhance your life